Schools are safer than they were in the 90s, and school shootings are not more common than they used to be, researchers say
The deadly school shooting this month in Parkland, Florida, has ignited national outrage and calls for action on gun reform. But while certain policies may help decrease gun violence in general, it’s unlikely that any of them will prevent mass school shootings, according to James Alan Fox, the Lipman Family Professor of Criminology, Law, and Public Policy at Northeastern.
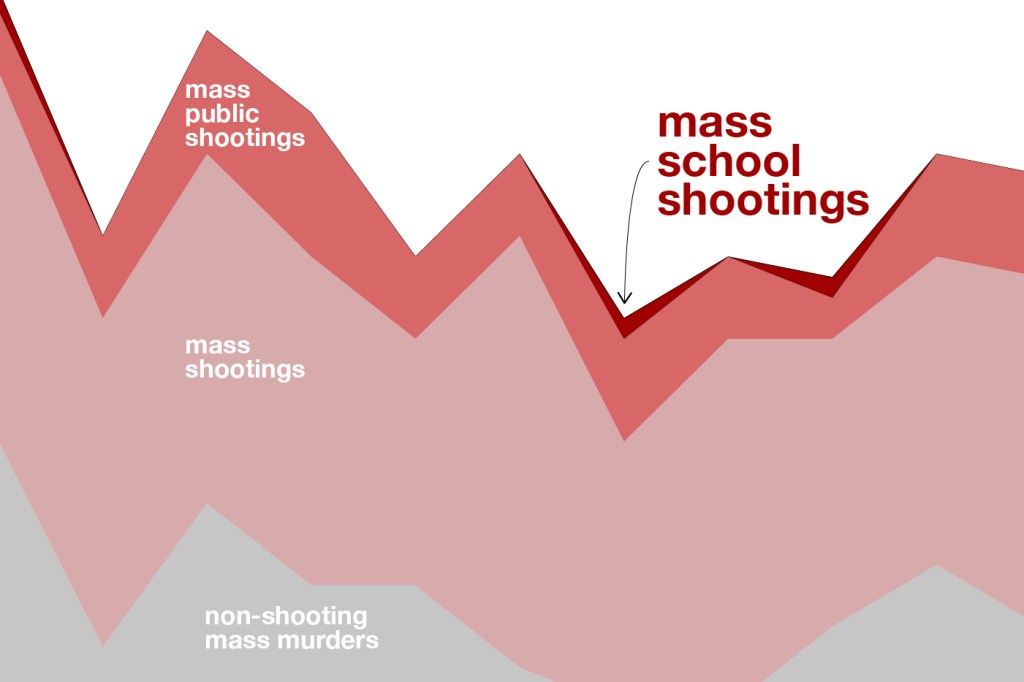
Since 1996, there have been 16 multiple victim shootings in schools, or incidents involving 4 or more victims and at least 2 deaths by firearms, excluding the assailant.
Of these, 8 are mass shootings, or incidents involving 4 or more deaths, excluding the assailant.
“This is not an epidemic”
Mass school shootings are incredibly rare events. In research publishing later this year, Fox and doctoral student Emma Fridel found that on average, mass murders occur between 20 and 30 times per year, and about one of those incidents on average takes place at a school.
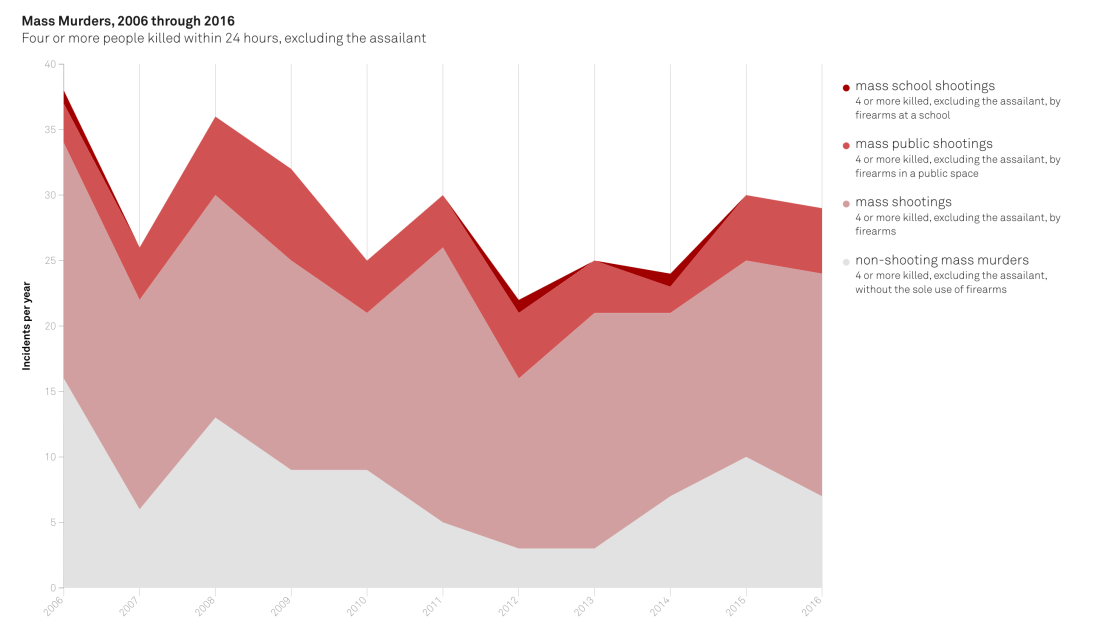
Fridel and Fox used data collected by USA Today, the FBI’s Supplementary Homicide Report, Congressional Research Service, Gun Violence Archive, Stanford Geospatial Center and Stanford Libraries, Mother Jones, Everytown for Gun Safety, and a NYPD report on active shooters.
Their research also finds that shooting incidents involving students have been declining since the 1990s.
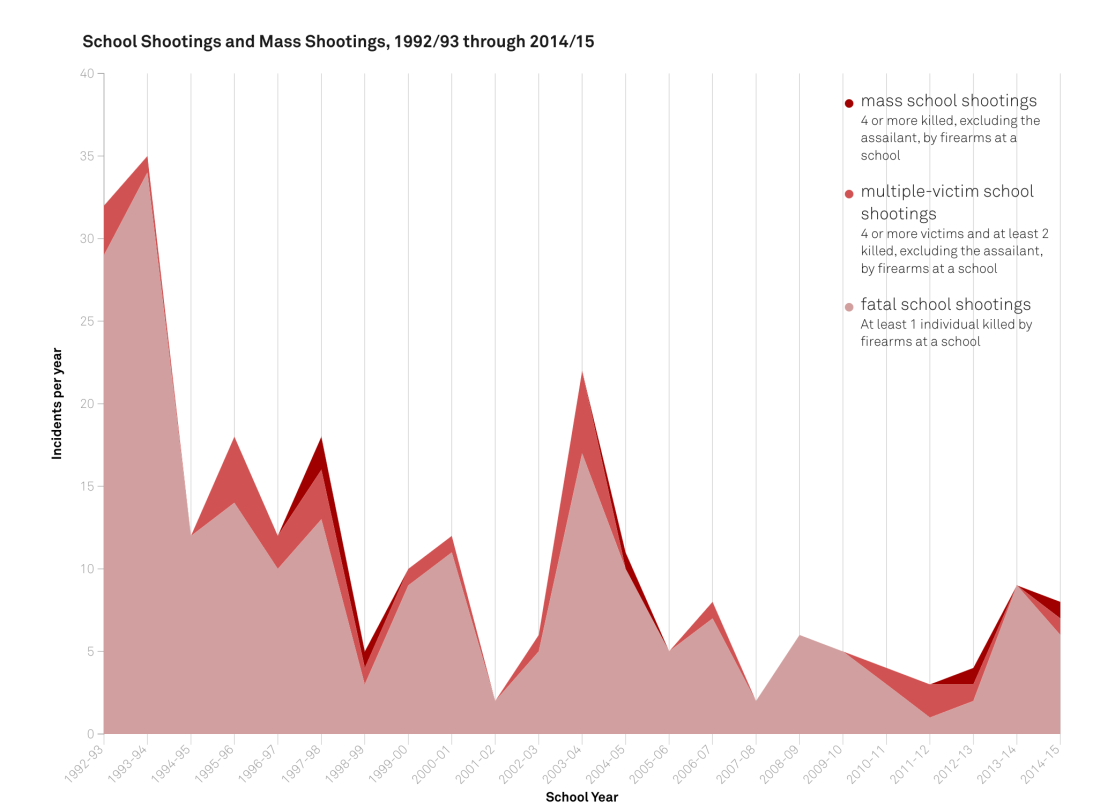
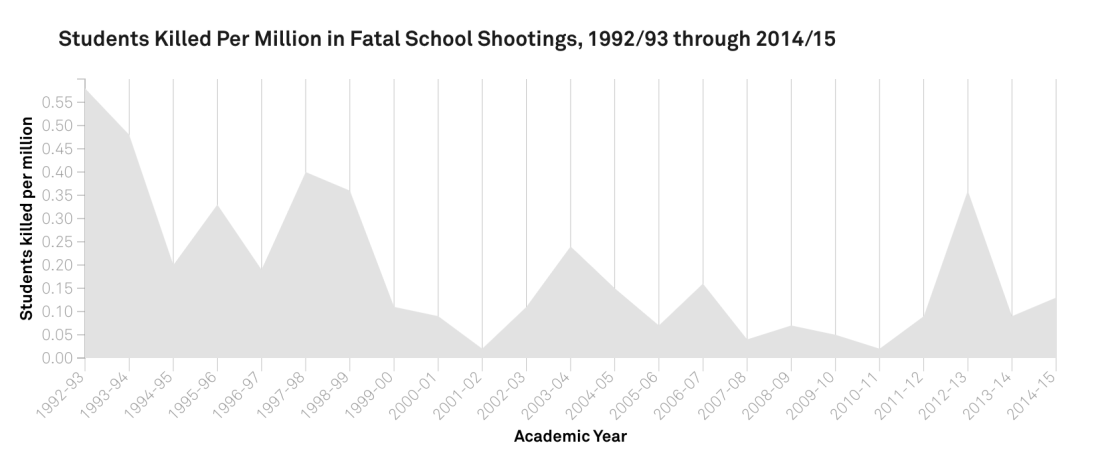
Four times the number of children were killed in schools in the early 1990s than today, Fox said.
“There is not an epidemic of school shootings,” he said, adding that more kids are killed each year from pool drownings or bicycle accidents. There are around 55 million school children in the United States, and on average over the past 25 years, about 10 students per year were killed by gunfire at school, according to Fox and Fridel’s research.
Fox said, however, some policy changes aimed at decreasing school shootings and gun violence in general certainly have merit. Banning bump stocks and raising the age of purchase for assault rifles from 18 to 21 are good ideas, and may lead to a decrease in overall gun violence, he said. But he doesn’t believe these measures will prevent school shootings. “The thing to remember is that these are extremely rare events, and no matter what you can come up with to prevent it, the shooter will have a workaround,” Fox said, adding that over the past 35 years, there have been only five cases in which someone ages 18 to 20 used an assault rifle in a mass shooting.
Fridel said increasing mental health resources for students is another strategy that might improve school safety, calling this a critical need that has been historically overlooked. She also said that the U.S. is facing a desperate shortage of guidance counselors. In 2014-15, the student-to-school counselor ratio was 482-to-1, according to the American School Counselor Association, nearly twice the organization’s recommended ratio.
“You might have students in a very large school who are troubled but who are basically flying under the radar, because you have one guidance counselor for 400 students,” Fridel said.
Should schools become fortresses?
After the Columbine High School shooting in 1999, schools across the country began holding active shooter drills in which they huddled together in a corner or hid under their desks. Such exercises—which may include someone walking around pretending to shoot students—can be very traumatic, Fridel said, and there is no evidence that they help protect students. “These measures just serve to alarm students and make them think it’s something that’s common,” she said.
Other safety precautions, such as installing metal detectors and requiring ID cards for entry, have also proven ineffective in past school shootings.
Fridel pointed to a few examples.
- In 1989, a shooter killed five and injured 32 elementary school children in Stockton, California, by targeting them on the playground.
. - In 2005, a 16-year-old killed seven people at his Minnesota high school by walking through the front door metal detector and fatally shooting a guard.
. - In a 1998 shooting in Jonesboro, Arkansas, two students pulled a fire alarm and began sniping people as they filed out to the parking lot, killing five and wounding 10 others.
In addition to being ineffective, Fox said increased security measures of these kinds can do more harm than good. He called the suggestion to arm teachers “absurd” and “over the top.”“I’m not a big fan of making schools look like fortresses, because they send a message to kids that the bad guy is coming for you—if we’re surrounding you with security, you must have a bull’s-eye on your back,” Fox said. “That can actually instill fear, not relieve it.”





